Orthopedic Implants: Enhancing the Quality of Life for Patients
Orthopedic implants and instruments are medical devices used in the treatment of musculoskeletal conditions, such as fractures, joint replacements, and spinal injuries. These devices are designed to restore function and mobility to the affected area, improving the quality of life for patients.
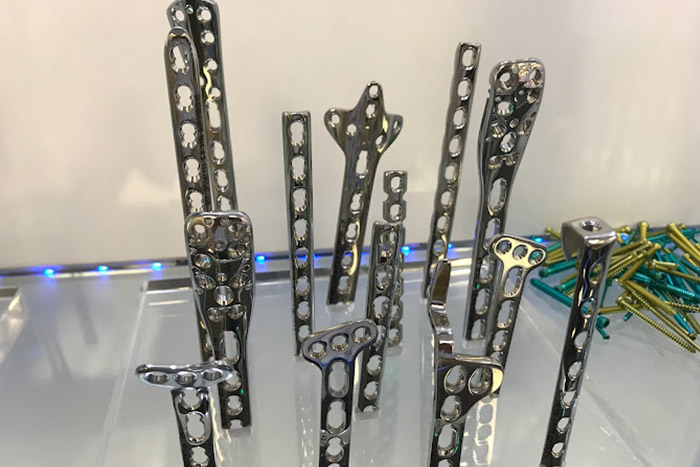

Orthopedic implants
Orthopedic implants are usually permanent medical devices that are surgically placed in the body to replace or support damaged or diseased bones, joints, or tissues. Common types of orthopedic implants include joint replacements, such as hip and knee replacements, as well as screws, plates, and rods used to stabilize fractures. Orthopedic implants are made of materials such as Stainless Steel, Titanium, ceramic, and plastic and are designed to be biocompatible with the human body.
Orthopedic instruments
Orthopedic instruments are specialized tools used by surgeons during orthopedic procedures. These instruments are designed to provide precise and efficient surgical intervention and may include a wide range of instruments such as forceps, scalpels, drills, and saws. Orthopedic instruments may be made of materials such as stainless steel, titanium, and plastic and are often sterilized before use to minimize the risk of infection.
Orthopedic implants and instruments play a vital role in the treatment of musculoskeletal conditions, helping to restore function and mobility to the affected area. These devices are designed to be biocompatible with the human body and are used by surgeons to provide precise and efficient surgical intervention.
The history of orthopedic implants dates back to ancient times, with the use of wooden splints and braces to support and stabilize broken bones. However, it was not until the 20th century that significant advancements were made in the development and use of orthopedic implants.
One of the earliest orthopedic implants was the Thomas splint, developed in the early 1900s by Dr. Arthur Steindler. This splint was made of metal and used to stabilize fractures in the lower leg. In the 1950s, Dr. John Charnley developed the first successful total hip replacement using a metal ball and socket joint. This pioneering surgery revolutionized the treatment of hip fractures and paved the way for further developments in joint replacement surgery.
In the 1960s, the first successful knee replacement surgery was performed using a plastic and metal implant. This marked a significant advancement in the treatment of knee injuries and osteoarthritis. In the 1980s, the use of biocompatible materials, such as ceramic and titanium, in orthopedic implants became more widespread. These materials are now commonly used in the production of joint replacements and other orthopedic implants.
In the 21st century, advancements in computer-aided design and 3D printing have further revolutionized the field of orthopedic surgery. These technologies have allowed for the production of custom-fit orthopedic implants, improving the precision and fit of these devices.
Overall, the history of orthopedic implants is marked by significant advancements in the design and materials used in these devices. From wooden splints to custom-fit implants made with biocompatible materials, orthopedic implants have greatly improved the treatment and recovery of musculoskeletal injuries and conditions.